Understanding the Environmental Potential of Batteries
In the realm of renewable energy and sustainable technology, batteries play a crucial role. From powering electric vehicles (EVs) to storing energy generated from renewable sources like solar and wind, batteries enable a cleaner and more efficient energy ecosystem. However, as with any technology, batteries come with their own set of environmental challenges, particularly concerning their production, use, and end-of-life management.
The Environmental Impact of Batteries
Firstly, let's examine the environmental impact of batteries:1. Production Phase
The extraction of raw materials for battery production, such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, often involves environmentally destructive practices like mining and deforestation. While battery technologies like LFP utilize less conflicted materials, there's still progress needed in optimizing the environmental and labor aspects of the value chain.
2. Use Phase
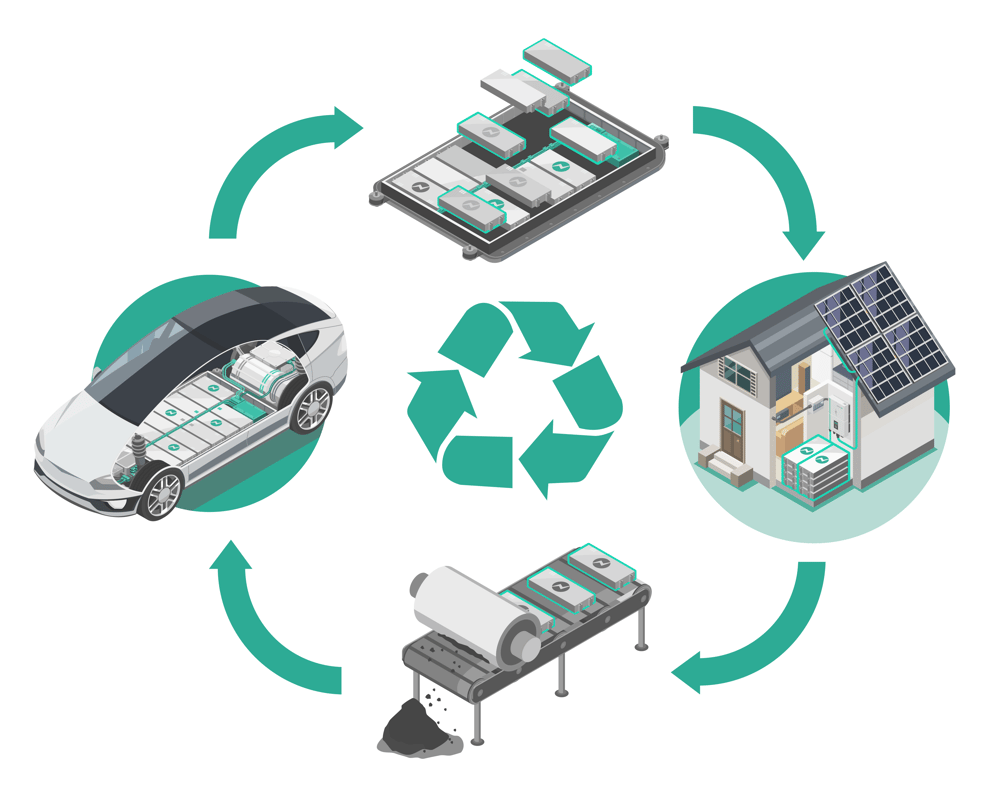
While batteries offer a cleaner alternative to fossil fuels when in use, their overall environmental impact extends beyond their operational lifespan. EV batteries, for example, degrade over time, with an average degradation level of 70%-80% at the end of their lifecycle in vehicles. Additionally, advancements in battery technology are leading to batteries that outlive the vehicles they power, presenting opportunities for extended use.
3. End-of-Life Management
Improper disposal of batteries can result in toxic chemicals leaking into soil and water, posing risks to ecosystems and human health. Low battery recycling rates exacerbate resource depletion and pollution, underscoring the need for improved recycling infrastructure.
The Importance of Recycling
Recycling offers a solution to mitigate the environmental impact of batteries by recovering valuable materials and reducing the need for virgin resources. However, challenges such as complex battery chemistries, economic factors, and regulatory issues hinder widespread recycling efforts. For example, one of the main benefits of LFP batteries, the absence of valuable materials such as cobalt and nickel, means that the materials extracted from recycling are not very valuable, leaving recycling of such batteries with low economic viability. However, it is not only the batteries that become more efficient, and great efforts are put into the development of recycling. By extending the batteries lifespan, society can allow for this development, saving both the batteries and money.
Second-Life Applications: Extending Battery Lifespan
An emerging approach to address the environmental impact of batteries is the concept of second-life applications, particularly in Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS). By repurposing batteries for stationary storage applications, second-life applications maximize battery value, delay recycling, and offer a more economically viable option for energy storage. In the transition to a sustainable energy future, second-life batteries also play a crucial role in promoting grid stability, circular economy principles, and reducing environmental impact.
Future Innovations in Battery Technology
As the importance of environmentally friendly practices continues to grow, so does the need for innovative battery technologies that minimize their environmental footprint. In the future, we can expect to see advancements in battery technology that focus on enhancing energy storage capacity, improving efficiency, and reducing the use of hazardous materials.
One of the areas of ongoing research and development is the exploration of alternative materials for battery production. Scientists and engineers are actively investigating the use of sustainable and abundant materials that can replace the currently used rare and expensive elements. This not only reduces the environmental impact but also makes batteries more economically viable and accessible.
Moreover, future innovations in battery technology may also include advancements in recycling techniques and processes. Researchers are working towards developing more efficient and cost-effective methods for recycling batteries, enabling the recovery of a higher percentage of valuable materials and reducing waste generation.
Overall, the future of battery technology holds great promise in terms of reducing environmental impact and creating a more sustainable energy storage solution.




